Linear kinematics¶
Description¶
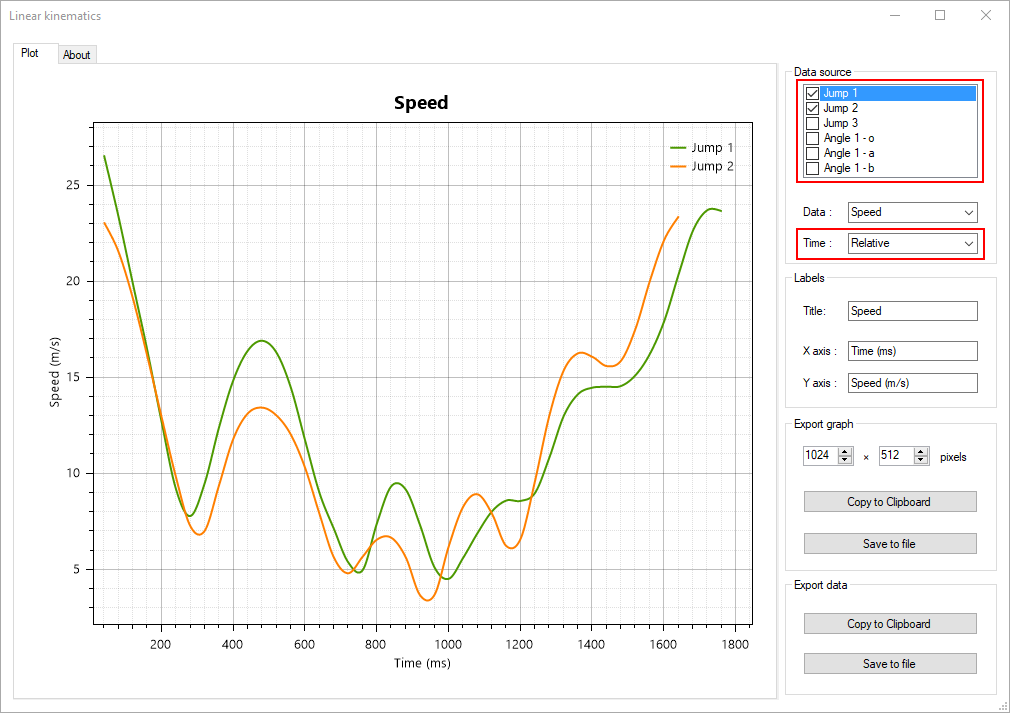
The linear kinematics diagram displays line charts of points trajectories and tracked objects points.
This can be used to study and compare the evolution of position, speed, or acceleration over time.
Data source¶
The data source list contains a list of all tracked points. Data from individual points can be hidden from the line chart by unchecking the checkbox in front of the point name.
Points in drawings with multiple points are listed by the name of their drawing and a point identifier.
Data type¶
The Data type drop down sets the kinematic quantity used in the line chart. The following options are available:
Horizontal position
Vertical position
Total distance
Total horizontal displacement
Total vertical displacement
Speed
Horizontal velocity
Vertical velocity
Acceleration
Horizontal acceleration
Vertical acceleration
Total horizontal displacement and total vertical displacement computes the resultant displacement between the first point and the current point of the trajectory. This is similar to the horizontal and vertical position but makes it relative instead of absolute.
Note
Be mindful that acceleration values are very sensitive to noise as they are the second derivative of the digitized position.
Time type¶
The Time type drop down sets the time scale used in the line chart. The following options are available:
Absolute: times are in normal video time.
Relative: times are expressed relative to the start of each trajectory.
Normalized: times are expressed as a fraction of each trajectory duration.
Relative time aligns events to their start, this can be used to compare trajectories that did not occur at the same time in the video.
Normalized time can be used to compare the shape of time series that did not last the same duration.
Export options¶
The data can be exported to an image or to tabular data. For tabular data the points are sorted by time; the first column is the time in milliseconds, the other columns are values from the time series.